Convert CAD data to GIS with ArcGIS Pro
Converting data built with a CAD program to GIS format is a very common routine, especially since engineering disciplines such as surveying, cadastre or construction still use files built in computer aided design (CAD) programs, with non-oriented construction logic. to objects but to lines, polygons, groupings and labels located in different layers (layers). Although the new versions of CAD software increasingly have an object-oriented approach with interaction with spatial databases, the compatibility between these disciplines still requires transformation processes.
What is expected to be obtained: extract the layers from a CAD file to GIS, to later perform analysis of the area, for this example we use a CAD file that contains information of cadastral properties, hydrographic information, that is Rivers and other structures built.
What you should have at the end of the process is a layer of land, a layer of rivers and a layer of structures, the initial format of each layer obeys the nature of the origin.
Available data and supplies: a CAD file, in this case a dwg of AutoCAD 2019.
Sequence of Steps with ArcGIS Pro
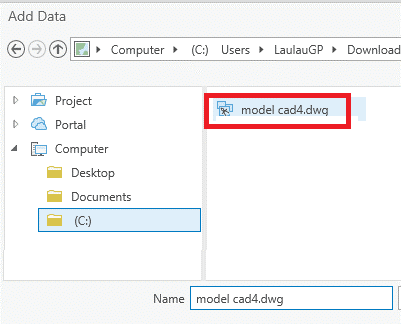
Step 1. Import the CAD file
As indicated above you must have a .dwg, .dgn or .dxf file, (CAD format), it is selected from the tab Map the option Add Data, there the corresponding file is searched. Here begins at this point the complication of displaying the data by the version of the file, there was a .dwg file in AutoCAD 2019, when the layer is entered into ArcGIS Pro, the system read the set of layers, but in the attribute table it appears that the layers do not contain any entity, as can be seen in the following figure.

When viewing the original file, in AutoCAD Civil3D it can be seen that it does have information.

Before believing that the file is corrupt or has no information, it is necessary to take into account the dwg versions accepted by ArcGIS Pro:
For .dwg and .dxf
- Reading, but not exported: 12 and 13 version of AutoCAD
- Direct reading and exported: Versions AutoCAD 2000 v15.0, 2002 v15.0, 2004 v16.0, 2005 v16.1, 2006 v16.2, 2007 v17.0, 2008 v17.1, 2009 v 17.2, 2010 v18.0, 2011 v18.1, 2012 v18.2, 2013 v19.0, 2014 v19.1, 2015 v 20.0, 2016 v20.1, 2017 v21.0 and 2018 v22.0.
For .dgn
- Reading, but not exported: MicroStation 95 v5.x, MicroStation SE v5.x, MicroStation J v 7.x
- Direct and exported reading: MicroStation V8 v 8.x
As you can see, at the time of preparing this tutorial, ArcGIS Pro still does not support reading and exporting data from AutoCAD 2019, so there is no display of entities in the view, the funny thing is that ArcGIS Pro does not indicate errors during the adhering of the layers, nor does it warn that the file is not compatible with the version. Load the information with the CAD structure but without data.
After identifying this, it has been necessary to use TrueConverter to transform the dwg file, in this case we have done it to the 2000 version.
Step 2. Convert data from CAD file to SHP
The layers that you want to extract are identified, if all CAD data is required, we must only export each element as a shape, when the CAD is selected, a tab appears. CAD Tools, in the tools you can find the process Copy Features, a panel opens showing the input and output parameters; the input is the selected layer, in this case plots, and the output can be a separate file or a geodatabase associated with the project, when you are sure the process is executed and the layer will be added to the content panel .shp.

Step 3. Analyze consistency of incomplete topologies
- There is also a gap, which is generated in a polyline format when the GIS (shape) is extracted. As the resulting shapes adopt the original format, the plots and the lagoon in this case, must be converted to polygons, depending on the case and the requirement
- For rivers, the process is carried out normally, however, it is found that the main river and its tributaries were made up of many segments. To join them, select the tab Edit - tool Go, and with this join the segments corresponding to the main river, and also each segment of its tributaries.
 You can also see that in the layer containing the rivers there is a line that, due to its shape and location, does not belong to this layer, it is eliminated, by editing the layer that was already created.
You can also see that in the layer containing the rivers there is a line that, due to its shape and location, does not belong to this layer, it is eliminated, by editing the layer that was already created.
Why do polylines and objects appear that do not match the geometries of the parcels? The ideal is from the CAD program to clean the layers of non-corresponding objects, however, for the purposes of this exercise it has been done in this way. As an example, the source file had a 3D block with a certain twist, coming from an AutoCAD Recap file, when represented in a 2D view it becomes a polyline.
In case the topologies are previously reviewed from the CAD file:

To extract existing polygons from the CAD (1), you can perform the following process as it was done regularly in ArcMap: right button on the layer - Data - Export Features, indicates the exit route and the polygon shape will appear in your content panel.
In this case, it was done with a layer of polygons that was originally in the CAD file, corresponding to the structures, however, when polylines are reviewed, two original polygons (2) were missing in the original CAD:

In the event that topologies from the CAD file are known:
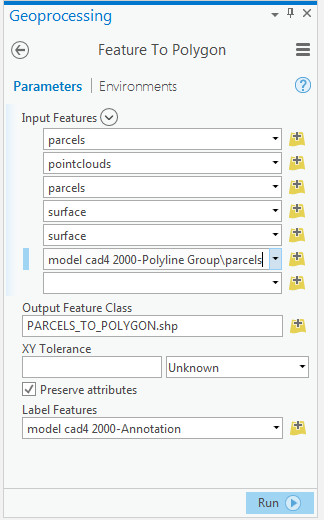
In the CAD Layers tab, the tool Feature to Polygon, this tool is used when there is certainty of the data coming from the CAD, we require them in polygon format. When executing the process, the panel is opened, where it asks to specify which or which are the layers or layers to be transformed.
- The box is checked if you want to preserve attributes of the CAD, ArcGIS Pro has reserved a number of fields with a specific style for this type of data.
- If the entities are associated with the annotations or labels of the CAD, these labels can be kept in the shape that is going to be created.
In this case, that the CAD file is a "topological crap", With the previous process it was possible to extract a single polygon, since the tool does not recognize the other structure because it is open, that is, it is not a complete polygon. for this the layer created with polygons is edited and the feature is created.
In the case of the lagoon, you can select the polylines that make it and use the tool to generate the shape with the polygon format.
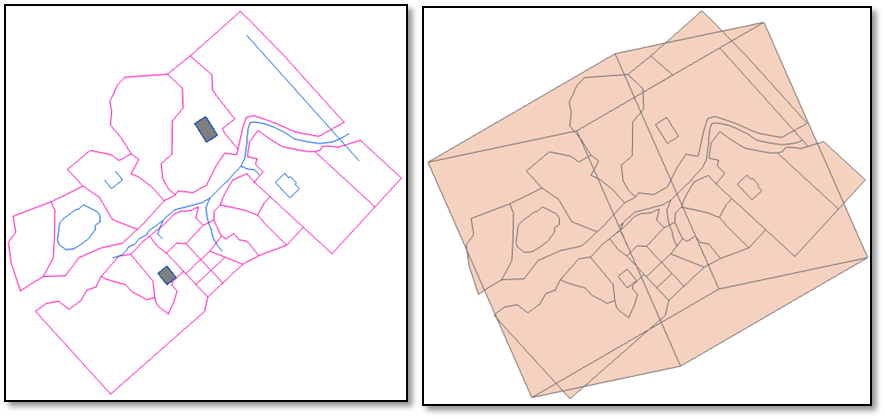
What happens with this tool, is that you must have total security of which elements are polygons; if not, it will generate a layer with topology errors, since entities of the layer intersect with each other, as shown in the example when trying to convert all CAD elements with this tool:
Controlled, in parts Automatic blind
Final score
After performing the corresponding processes for each layer we will have the following:
The shape of plots in polygon format

The rivers in polyline format

Buildings in polygons format

The lagoon in polygon format.

Now we can work and perform the required analysis, take into account the importance of the origin of the data, both its format and its topological consistency. Download here the output result.

This lesson has been taken from the 13 lesson of the Easy ArcGIS Pro course, which includes the video and step-by-step explanation. The course is available in English y in Spanish.